Radiologist-AI interaction
The aim of this project is to investigate if eye-tracking devices installed to radiologist workspaces can improve the diagnostic accuracy. This project will target the problem of fatigue estimation and diagnostic error prediction with eye-tracking.
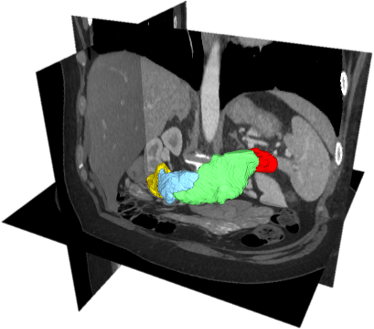
Pancreatic cancer surgery
Pancreatic cancer is currently the 4th and projected to be the 2nd leading cause of cancer-related death in developed countries. Pancreatic cancer is often detected on late stages and the percentage of unsuccessful/exploratory tumor removal attempts can vary from 24% to 63% for different hospitals in European countries. This project applies machine learning solution for improving pancreatic cancer treatment. The particular aims are to automatically segment pancreatic tumor, pancreas subparts, and abdominal vasculature, improve cancer visualization and access the surgery success attempts. The project will also evaluate the benefits of augmenting pancreatic cancer surgery with other treatment modalities.
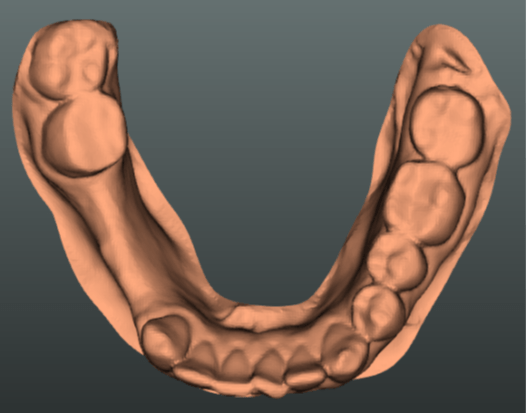
Dental procedures
The total number of dental procedures by a large margin surpasses the total number of other clinical procedures and treatments. Even a small improvement in caries diagnosis accuracy and implantation planning could result in significant savings for the healthcare system. This project aims to develop machine learning solutions for caries and root canal treatment planning.
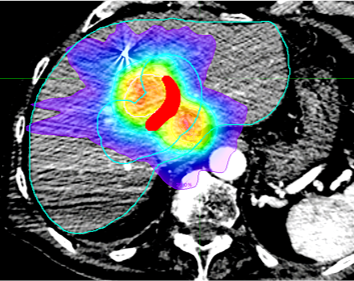
AI for radiotherapy planning
Radiation dose kills both cancer and healthy tissue cells. The modern radiotherapy equipment allows high personalization of dose delivery, which however does not allow complete sparing of healthy organs surrounding the tumor and up to 27% of treatment result in radiation-induced toxicities. It is very challenging to predict if a radiotherapy will result in toxicities. This research project develops machine learning solutions for the analysis of pre-radiotherapy medical images, spatial relationships among tumors and surrounding organs-at-risk, prescribed dose plans, concurrent-to-radiotherapy treatments and patient’s profile for the prediction of radiotherapy outcomes.
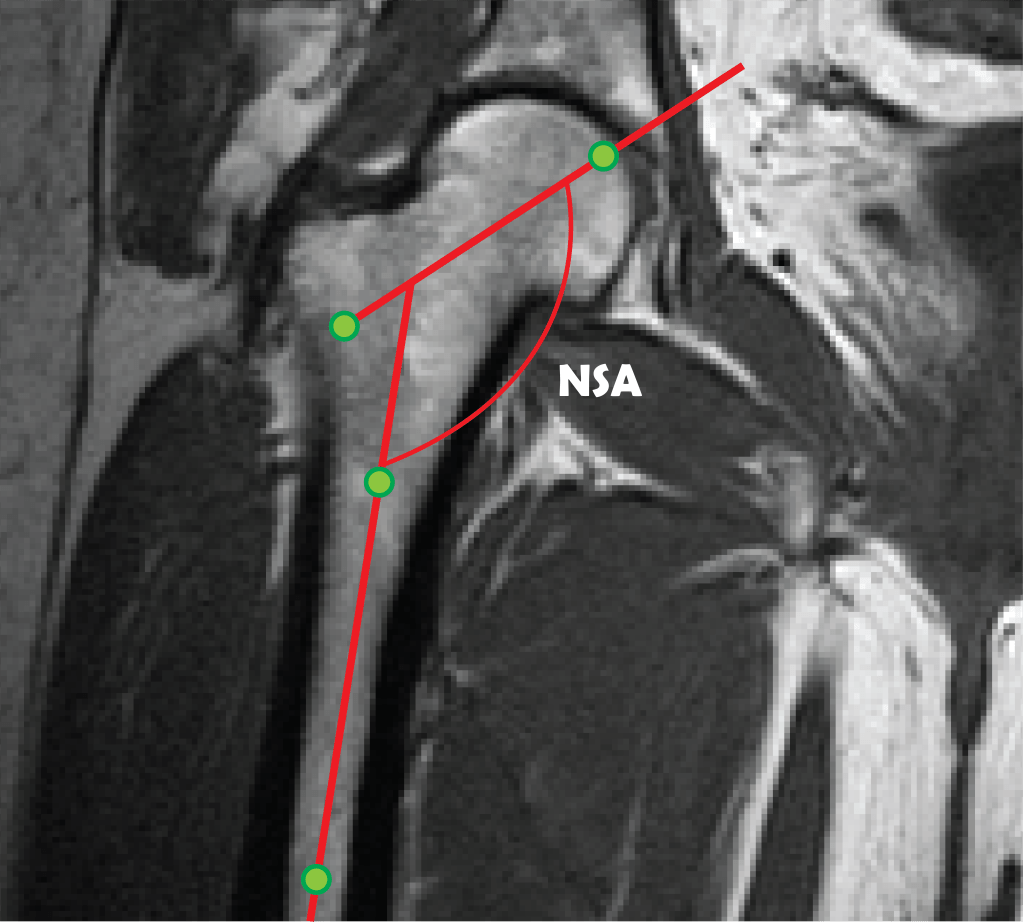
Morphological analysis of pelvic images
Musculoskeletal disorders accounts for most of the idiopathic pain cases worldwide. Diagnosis of musculoskeletal disorders is hampered due to the fact that early disorder stages often progress asymptomatically with up to 25% of mid-age adults having femoroacetabular abnormalities without experiencing any discomfort. This project combines machine learning with shape analysis for early diagnosis and quantification of spinal and pelvic abnormalities.
This work has been supported by the RFBR under grant 19-37-51034
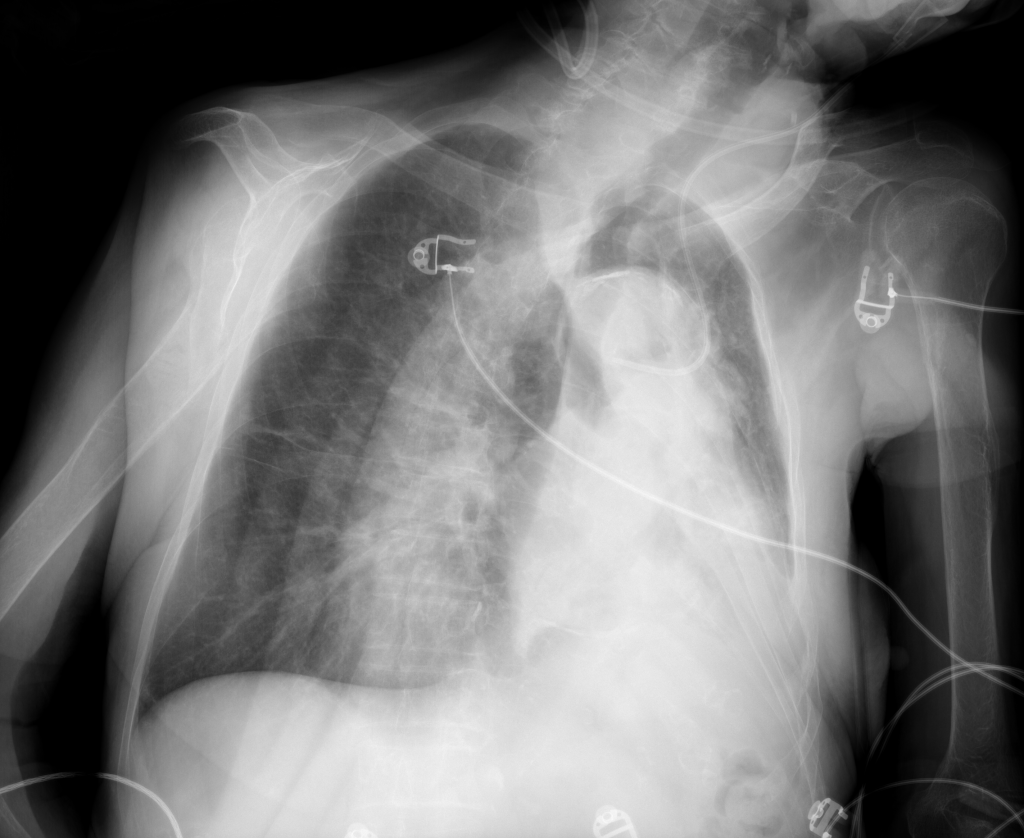
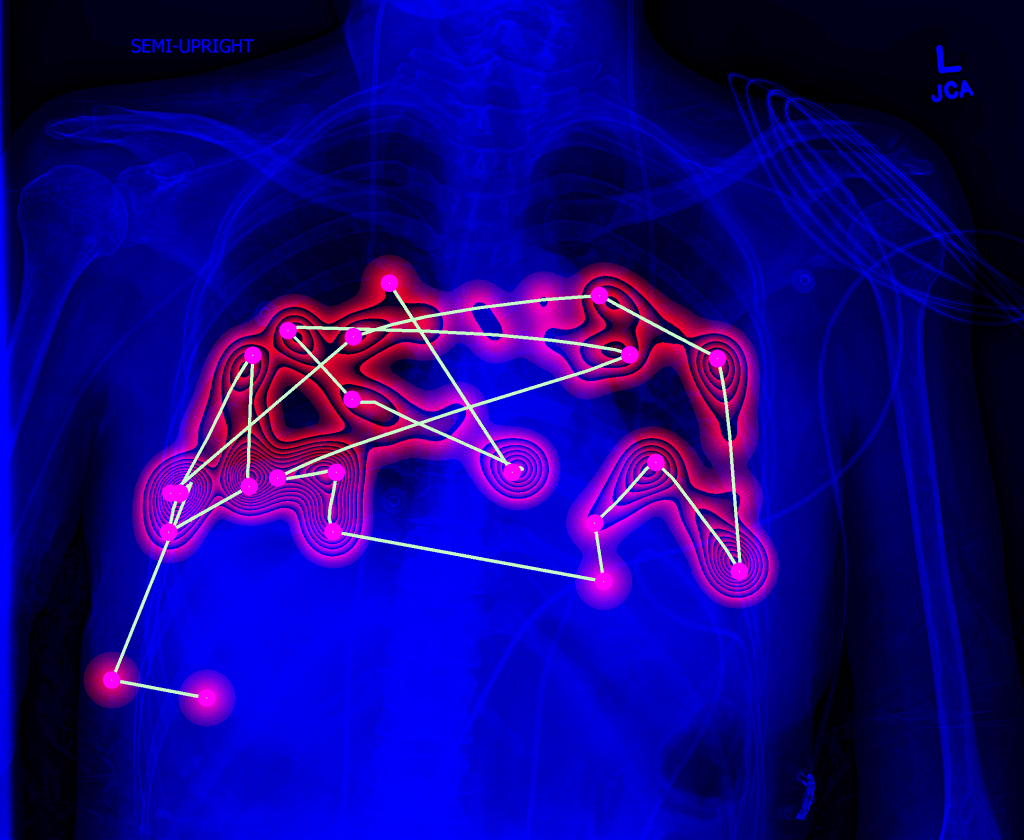
Lung image analysis
Chest X-rays is the most commonly acquired medical image worldwide. The advances of machine learning allow automated diagnosis of main lung pathologies, such as pneumonia and pneumothorax, with close-to-human performance. The automated diagnosis still however fails on patients with rare pathology manifestations, which precludes clinical integration of computerized solutions. The aim of this project is to develop solutions that will interact with physicians to improve lung disease diagnosis.